 When a person who lives in New York dies without a will, the state law of intestacy applies. This means that an administration petition must be brought and since there is no will stating the decedent’s last wishes, the law dictates who gets what. Although the proceedings are similar, there are some differences. Some are superficial: what people refer to as “beneficiaries” during a probate proceeding are actually distributees in an administration proceeding, the former executor is now called an administrator. Yet, in an administration proceeding the administrator is appointed by law, specifically Surrogates Court Procedure Act (SCPA) 1001, “Order of Priority for Granting Letters Administration”. This is an invitation for fiduciary appointment contests. A common example comes when the surviving spouse has predeceased and there are multiple children. When these children oftentimes cannot come to an agreement on who should be appointed, estate litigation ensues and estate litigation is not inexpensive. The easy remedy for this is creating a will and appointing an executor and successor executor, but oftentimes it is too late for that antidote. Regardless, these things happen and it is not the end of the world when they do. Everything can be dealt with.
When a person who lives in New York dies without a will, the state law of intestacy applies. This means that an administration petition must be brought and since there is no will stating the decedent’s last wishes, the law dictates who gets what. Although the proceedings are similar, there are some differences. Some are superficial: what people refer to as “beneficiaries” during a probate proceeding are actually distributees in an administration proceeding, the former executor is now called an administrator. Yet, in an administration proceeding the administrator is appointed by law, specifically Surrogates Court Procedure Act (SCPA) 1001, “Order of Priority for Granting Letters Administration”. This is an invitation for fiduciary appointment contests. A common example comes when the surviving spouse has predeceased and there are multiple children. When these children oftentimes cannot come to an agreement on who should be appointed, estate litigation ensues and estate litigation is not inexpensive. The easy remedy for this is creating a will and appointing an executor and successor executor, but oftentimes it is too late for that antidote. Regardless, these things happen and it is not the end of the world when they do. Everything can be dealt with.
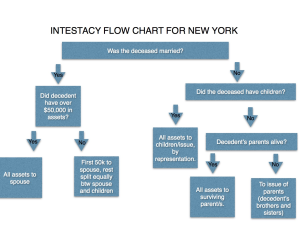
This law of intestacy in New York is codified in Estate Power and Trust Law (EPTL) § 4-1.1:
“The property of a decedent not disposed of by will shall be distributed as provided in this section. In computing said distribution, debts, administration expenses and reasonable funeral expenses shall be deducted but all estate taxes shall be disregarded, except that nothing contained herein relieves a distributee from contributing to all such taxes the amounts apportioned against him or her under 2-1.8. Distribution shall then be as follows: (a) If a decedent is survived by:
(1) A spouse and issue, fifty thousand dollars and one-half of the residue to the spouse, and the balance thereof to the issue by representation.
(2) A spouse and no issue, the whole to the spouse.
(3) Issue and no spouse, the whole to the issue, by representation.
(4) One or both parents, and no spouse and no issue, the whole to the surviving parent or parents.
(5) Issue of parents, and no spouse, issue or parent, the whole to the issue of the parents, by representation.
(6) One or more grandparents or the issue of grandparents (as hereinafter defined), and no spouse, issue, parent or issue of parents, one-half to the surviving paternal grandparent or grandparents, or if neither of them survives the decedent, to their issue, by representation, and the other one-half to the surviving maternal grandparent or grandparents, or if neither of them survives the decedent, to their issue, by representation; provided that if the decedent was not survived by a grandparent or grandparents on one side or by the issue of such grandparents, the whole to the surviving grandparent or grandparents on the other side, or if neither of them survives the decedent, to their issue, by representation, in the same manner as the one-half. For the purposes of this subparagraph, issue of grandparents shall not include issue more remote than grandchildren of such grandparents.
(7) Great-grandchildren of grandparents, and no spouse, issue, parent, issue of parents, grandparent, children of grandparents or grandchildren of grandparents, one-half to the great-grandchildren of the paternal grandparents, per capita, and the other one-half to the great-grandchildren of the maternal grandparents, per capita; provided that if the decedent was not survived by great-grandchildren of grandparents on one side, the whole to the great-grandchildren of grandparents on the other side, in the same manner as the one-half.
(b) For all purposes of this section, decedent’s relatives of the half blood shall be treated as if they were relatives of the whole blood. (c) Distributees of the decedent, conceived before his or her death but born alive thereafter, take as if they were born in his or her lifetime. (d) The right of an adopted child to take a distributive share and the right of succession to the estate of an adopted child continue as provided in the domestic relations law. (e) A distributive share passing to a surviving spouse under this section is in lieu of any right of dower to which such spouse may be entitled”
The statute is wordy, but it’s all there. In most cases the estate will pass to the spouse and children, but everyone’s situation is different. Life is not static though. Also see my previous post here: the statutory results of EPTL 4-1.1 may not be what you would have wished. Any questions regarding your specific situation can be asked in my Contact page.
